Cycling has become an increasingly popular form of transportation and exercise. Whether you’re a seasoned pro or just starting out, navigation apps can be a great tool to help you plan and navigate your routes. In this post, I’ll take a closer look at some of the cycling navigation apps and sites. The focus is the importing of GPX files, for instance routes downloaded from the Lake Trails’ website, and on mobile friendly solutions.
But first a bit more about navigation in general. In the world of modern cycling, navigation plays a pivotal role in ensuring a smooth and enjoyable ride. Thanks to advancements in technology, cyclists now have access to a powerful tool known as GNSS (Global Navigation Satellite System). GNSS refers to a network of satellite-based navigation systems that provide precise positioning, navigation, and timing information. By leveraging multiple satellite constellations, including, but not limited to, GPS, GLONASS, and Galileo, GNSS offers cyclists an array of benefits to enhance their riding experiences.
Commonly used GNSS Systems
The primary GNSS system that most cyclists are familiar with is GPS (Global Positioning System), it is a satellite-based navigation system owned and operated by the United States government. It consists of a network of orbiting satellites that transmit signals to GPS receivers on Earth. These receivers then calculate the user’s precise location, speed, and time information by analysing the signals received from multiple satellites.
In addition to GPS, there are other global navigation satellite systems, the most well-known of which are: GLONASS (Globalnaya Navigatsionnaya Sputnikovaya Sistema) and Galileo. GLONASS is owned and operated by the Russian Federation, while Galileo is owned and operated by the European Union.
GLONASS operates similarly to GPS, providing global positioning and navigation services. It utilizes a constellation of satellites to transmit signals to receivers, allowing users to determine their precise location.
Galileo, on the other hand, is Europe’s independent satellite navigation system. It aims to provide highly accurate positioning, navigation, and timing services to users worldwide. Galileo’s constellation of satellites works in conjunction with ground-based control centres and user receivers to enable accurate and reliable navigation.
Benefits for Cyclists
The utilization of GNSS systems brings numerous advantages to cyclists, particularly when it comes to navigation and route planning. By harnessing signals from multiple satellite constellations, GNSS-enabled devices, such as dedicated cycling GPS units or smartphones, can offer enhanced accuracy, improved signal reception, and better positioning in challenging environments. This proves invaluable for cyclists exploring unfamiliar territories, riding through dense urban areas, or venturing into remote regions with limited visibility.
The combination of GNSS systems expands the satellite coverage, reducing the likelihood of signal loss or inaccuracies that can occur when relying solely on one system. Cyclists can expect more reliable turn-by-turn directions, precise tracking of routes, and accurate distance and speed measurements. Moreover, the availability of multiple GNSS systems improves resilience against signal interference, allowing for uninterrupted navigation even in areas with obstructed views of the sky.
Additionally, GNSS-enabled devices provide cyclists with a wealth of data and analysis tools. Detailed ride metrics, such as elevation gain, cadence, heart rate, and power output, can be seamlessly integrated with GNSS data to offer comprehensive insights into performance and progress. This data-driven approach empowers cyclists to optimize training, set goals, and monitor improvements over time.
Apps and sites
Over the years, I have used all the apps mentioned in this post, as well as many others that are not mentioned, for both testing and data collection purposes. For a long time now, I have used Komoot for planning a route and Locus Map (classic) for tracking that route, in effect the latter is a backup system as I use a dedicated head unit for navigation, recording my rides, and following routes. When I first rode a multi-day ride, I had planned the route via cycle.travel, and opened the resulting GPX file in Locus Map. As I didn’t have a dedicated head unit at the time, I had placed my 20-years old Garmin eTrex on an improvised handlebar holder, and ‘followed’ the line on the screen. As that device does not have integrated maps, I reverted to my phone, and Locus Map, when needed, specifically in and around more urban areas.
Note that it is important to use cycling navigation apps responsibly. Please do not hold your phone in your hands while cycling and steering with the other hand. This can be very dangerous and increases the risk of accidents. Always remember to stop in a safe place, look at the map or directions, and then continue cycling. As experienced as I am, if I have a need to look at my phone, I still stop, look at the phone, tuck it away again, and only then continue cycling. Your safety and the safety of others on the road is of utmost importance.
Allow me to point out that when importing GPX files into some apps and websites, specifically route planning applications, the routes may be adjusted to what the software considers the best option. This can result in some changes to the original route. Please be aware that this is a common feature of GPS routing and navigation systems, and it is intended to provide you with the most accurate and efficient route possible. However, it is important to review the imported route carefully, and adjust where needed, to ensure that it meets your needs and preferences before embarking on your journey. Please use these tools responsibly and always exercise caution and common sense while navigating.
There are, of course, many, many apps and sites to choose from, and I shall focus only on a few, but see these as the starting point for your own journey into finding the method that works best for you.
In-browser solutions
GPS technology has made navigation easier and more accessible than ever before, and web-based GPS mapping solutions have made it even easier to plan and navigate routes on the go.
Google Maps
Google Maps is one of the most widely used GPS mapping solutions on the web, and for good reason. It offers a comprehensive range of features, including turn-by-turn navigation, real-time traffic updates, and a wealth of information about points of interest. Although not directly, Google Maps does allow users to import their own GPX files. And therefore, stands as a relatively simple solution for those who only need this functionality occasionally, who want to use something familiar, and who do not want to install a dedicated application.
To import a GPX file into Google Maps, go to Google My Maps and log in, click on Create A New Map, and you can then import a GPX file by clicking on the Import button and selecting the file from your computer or smartphone. Once imported, you can use Google Maps to view and edit your route. You can also see the route displayed as well as your own relative position to it.
Besides viewing this map now in the browser, if you have the Google Maps app installed on your smartphone, you can view and use it there too. Open the Google Maps app, at the bottom click on Saved, click on Maps, and select your imported map.
gpx.studio
gpx.studio is a web-based GPX editor that allows users to create, edit, and share GPX files. It offers a range of features, including the ability to add and edit waypoints, tracks, and routes, as well as the ability to export GPX files. You can also import a previously downloaded GPX file.
To use gpx.studio, start by visiting their website, click on Load GPX and the route will appear on screen. If you can’t find the Load GPX button, for instance on a mobile device, then click on the ‘Hamburger menu’ at the top, and you will see it. You will also notice that you now have the route of your choice on screen, and if you have allowed your browser to locate your position, you will see that too relative to the route, ready for you to follow.
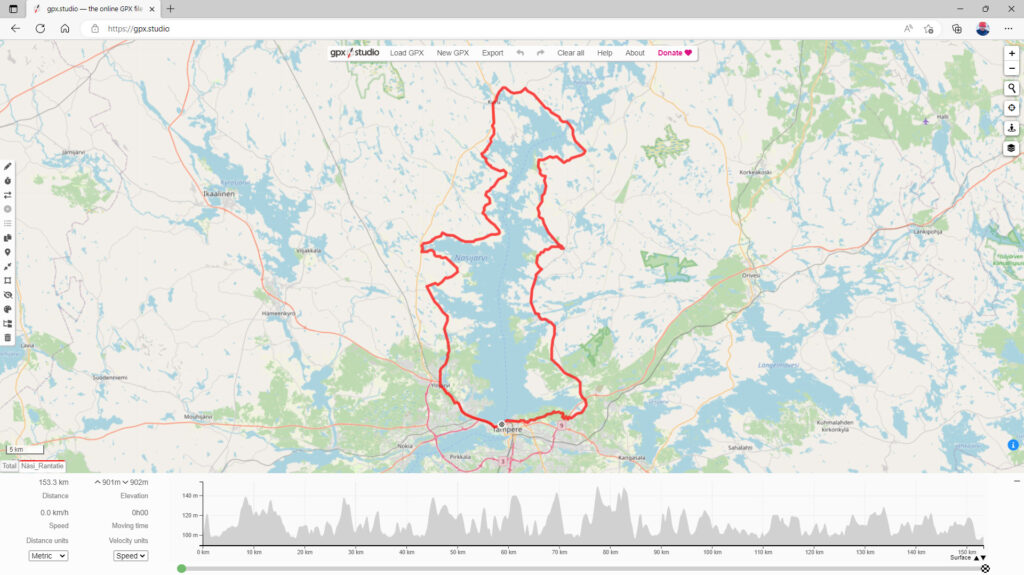
cycle.travel
cycle.travel is a web-based GPS mapping solution that’s specifically designed for cyclists. It offers a range of features, including turn-by-turn navigation, elevation profiles, and the ability to plan and save routes. cycle.travel also allows users to import and export GPX files, which makes it a great choice for those who want to plan and navigate their own cycling routes.
To import a GPX file into cycle.travel, start by visiting their website and creating an account. Once logged in, you can create a new route by clicking on the My ‘bicycle’ button on the navigation bar on top. From there, click on Journeys and then on upload a GPX route under the Upload section. Once imported, you can use cycle.travel to view and edit your route, as well as get turn-by-turn directions and other information about your route.
Mapping apps
GPS technology has revolutionized the way we navigate the world, and with the advent of smartphones, GPS mapping software has become more accessible than ever.
Locus Maps (4 or classic)
Locus Maps is a comprehensive GPS navigation app that allows users to download and store maps for offline use. It offers a wide range of features, including route planning, location tracking, and real-time navigation. The app is available in both a free and a paid version, with the paid version offering more advanced features such as backup and syncing, live tracking, and offline routing.
To use Locus Maps, start by downloading the app from the App Store or Google Play. Once installed, you’ll need to download a (or select an online) map for the area you plan to navigate. You can then plan your route, either by selecting points on the map or by importing a pre-planned route. Locus Maps will then guide you along your route, providing turn-by-turn directions and real-time information about your location.
To import a GPX file, click on the menu button, then Tracks & Routes, and then on the +-sign at the bottom, select Import and select your GPX file to import. Once imported you can see the route and your current position on screen.
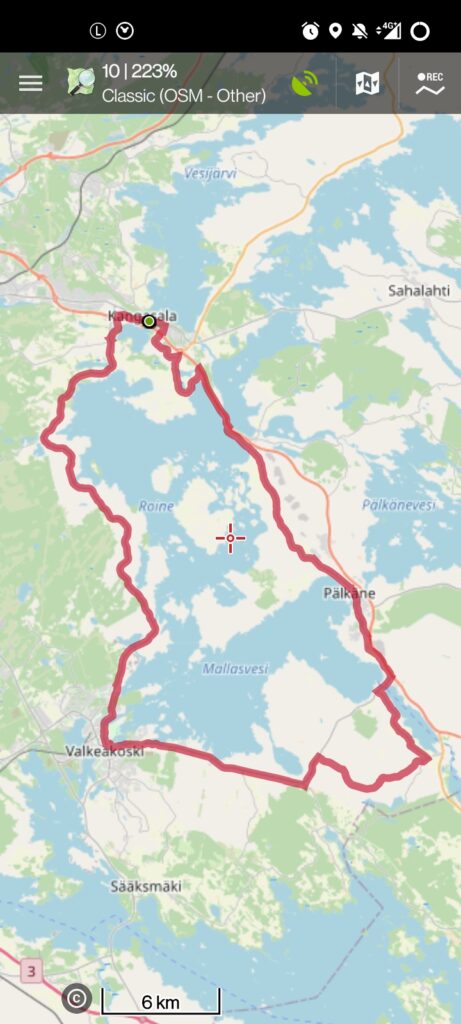
OsmAnd+
OsmAnd+ is another popular GPS mapping app that offers both online and offline maps. It’s based on OpenStreetMap data, which is a crowdsourced mapping platform that provides free, open-source maps of the world. OsmAnd+ offers a range of features, including turn-by-turn navigation, offline map storage, and route planning.
To use OsmAnd+, start by downloading the app from the App Store or Google Play. Once installed, you’ll be presented with the opportunity to download the map for the area you plan to navigate. This is part of the initialisation process but can be done later by searching for the area in the app and selecting the appropriate map. You can then plan your route by selecting points on the map or by importing a pre-planned route. OsmAnd+ will then guide you along your route, providing turn-by-turn directions and real-time information about your location.
Importing and showing GPX routes on the map can be a bit daunting at first, but it’s not that complicated. Click on the menu button, select Plan a route, and then Import track. Select the file that you want to import, and then Save in the top right corner. After you have saved the imported route, you’ll notice that it is not visible on the map. Click the menu button again and select Configure map. Select the 3 dots after Tracks, click on All and select your just imported route, hit Apply, and go back to the map. Now it is visible, as well as your current position.
Komoot
Komoot is a GPS mapping app that’s specifically designed for outdoor activities such as hiking, cycling, and mountain biking. It offers a wide range of features, including offline map storage, turn-by-turn navigation, and the ability to discover new routes based on user preferences. Komoot is available in both a free and a paid version, with the paid version offering more advanced features such as a multi-day planner, sport-specific maps, and live tracking.
To use Komoot, start by downloading the app from the App Store or Google Play. Once installed, you’ll need to create an account and select your preferred activity type. You can then search for routes in your area, either by selecting a pre-planned route or by creating your own. Komoot will then guide you along your route, providing turn-by-turn directions and real-time information about your location.
To import and use a downloaded GPX file, open Komoot and click on Profile, then click on the +-sign next to Tours. Select the Import a file option and select the file that you want to import. Follow the next few steps, and then you’ll be presented with your imported route, ready for navigation. Note that Komoot does need you to buy maps of regions, so this may not be the best option for an occasional or first-time user, although it does allow for the download of one free region.
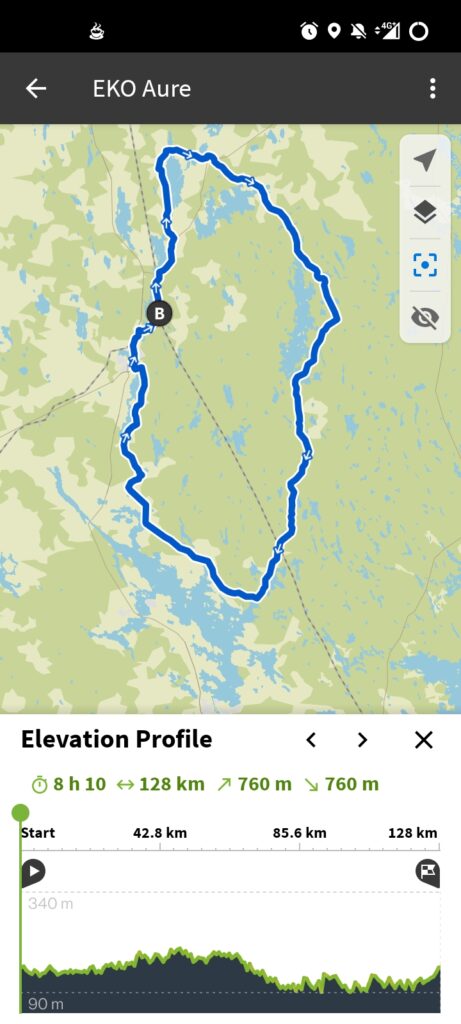
GPX Viewer
GPX Viewer is a simple yet powerful app for viewing and analysing GPX files. It allows you to open GPX files and view them in detail. GPX Viewer displays your route on a map, complete with elevation profiles and other useful information.
To use GPX Viewer, simply download the app and open the GPX file you want to view. You can then explore your route on the map and analyse its features using the app’s tools.
To view a downloaded GPX file on the map, simply press the menu button, and click on Open files. Browse to the folder where your download file is, select it, and click on Open. The track is now visible on screen relative to your position.
Sporty apps & data analysis
For many athletes, tracking and analysing their training is an essential part of their routine. Apps like Strava and TrainingPeaks offer a range of features to help athletes plan and track their workouts, analyse their performance, and set and achieve their goals. Whilst the intervals.icu website does a similar, if not better job.
Strava
Strava is a popular app among runners and cyclists for tracking workouts, sharing routes, and its social aspect, connecting with other athletes. It offers a range of features to help you plan and track your workouts, including GPS tracking, heart rate monitoring, and segment tracking.
To get started with Strava, simply download the app and create an account. Once logged in, you can start tracking your workouts using your phone or GPS-enabled device. Strava offers both free and paid versions of their app, with the paid version offering additional features such as training plans, segments, and advanced analytics.
TrainingPeaks
TrainingPeaks is a popular app among triathletes and other endurance athletes for tracking and analysing their training. It offers a range of features to help athletes plan and track their workouts, including custom training plans, heart rate monitoring, and performance analysis.
To use TrainingPeaks, create an account, either online or in the app, and start building your training plan. You can then track your workouts using your GPS-enabled device and analyse your performance using the app’s tools. TrainingPeaks offers both free and paid versions of their app, with the paid version offering additional features such as advanced analytics, custom coaching, and the ability to plan more than 2 days ahead in the training calendar.
Intervals.icu
Intervals.icu is an online platform catering to athletes, coaches, and sports enthusiasts involved in endurance sports like running, cycling, swimming, and triathlons. It serves as a centralized hub for importing and analysing data from fitness trackers, GPS devices, and smartwatches. By offering comprehensive visualizations and advanced analytics, the platform provides valuable insights into an athlete’s performance, helping them make informed decisions and optimize their training routines.
With Intervals.icu, users can import data from various devices, including training sessions, races, heart rate data, power output, and more. The platform generates interactive visualizations that showcase an athlete’s progress over time, enabling them to identify trends and areas for improvement. It also utilizes algorithms to derive metrics like training load, intensity distribution, and fitness trends, giving athletes quantitative measures to adjust their training plans and enhance their performance.
Intervals.icu fosters a sense of community by allowing athletes to connect with others, join training groups, and share achievements. This social aspect encourages knowledge sharing, support, and friendly competition among users. Overall, Intervals.icu offers a comprehensive and user-friendly solution for athletes and coaches, helping them analyse data, set goals, and optimize their training for better endurance sports performance.
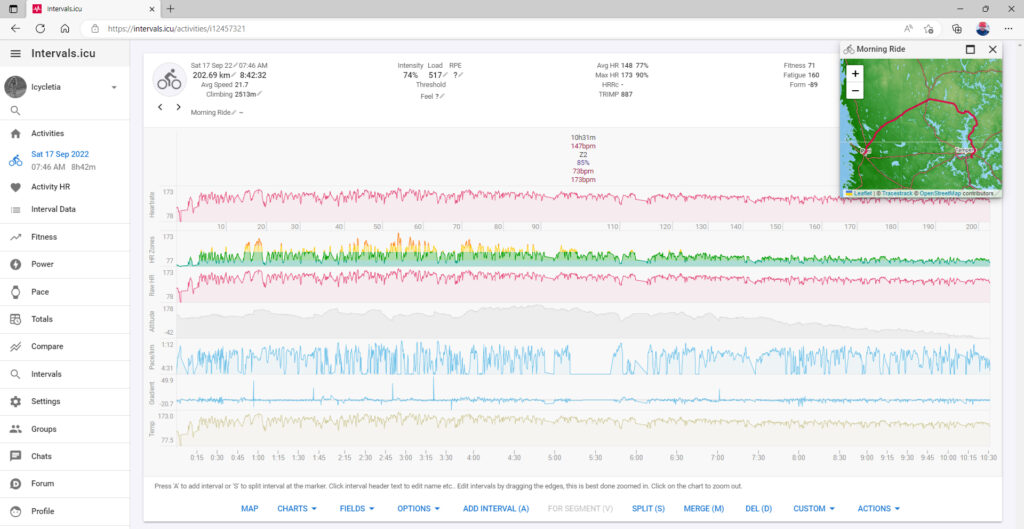
Final thoughts
The world of cycling apps and websites offers a vast array of options for navigation, data analysis, and tracking. While this post focused on a select few, it’s important to note that there are numerous other valuable tools available. Whether you’re a casual cyclist or a serious athlete, these apps and websites can greatly enhance your cycling experience by providing valuable insights, improving training routines, and helping you navigate new routes with confidence. Explore the wide range of options out there and find the ones that best suit your needs and preferences.
Happy cycling!

